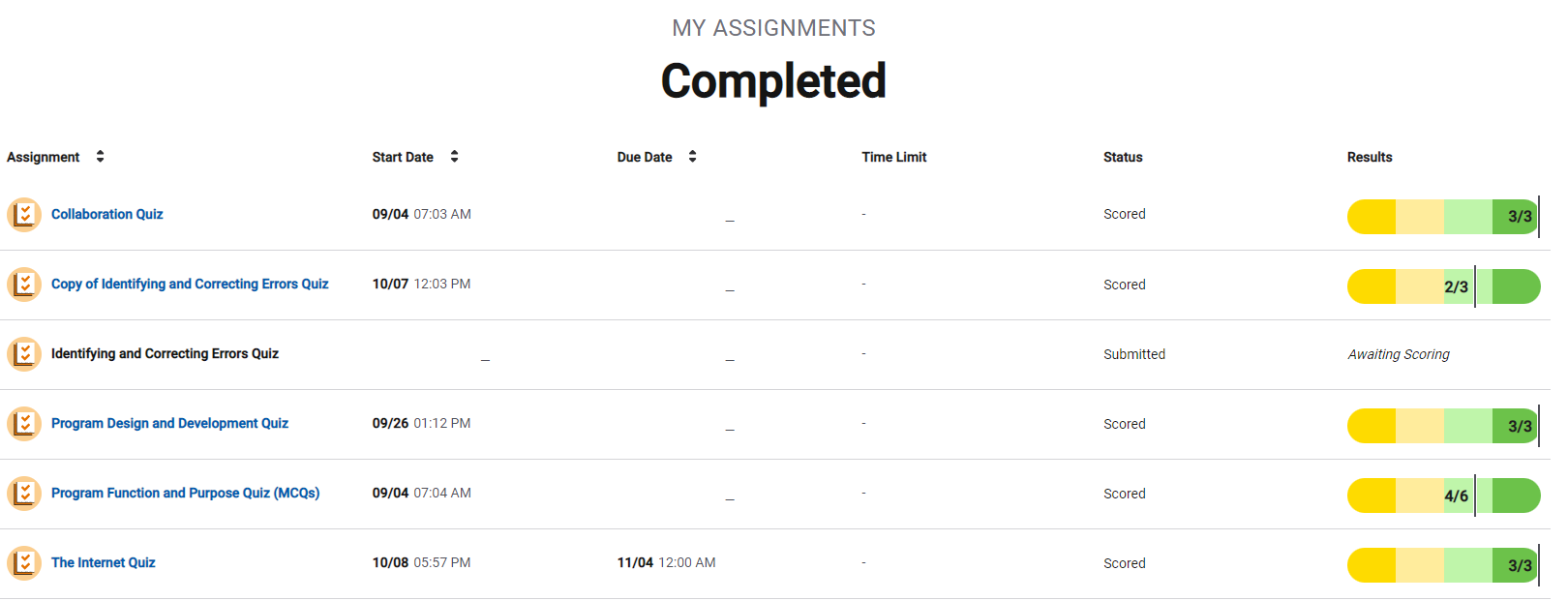
AP Classroom Completed Assignments (10/17)
AP Classroom Completed Assignments (10/17)
The AP Classroom Completed Assignments for this week.
4.1
- Computers used to be very large, and take up full rooms because of how big they were
- Computers got smaller as time progressed
- Computers needed to connect to each other in order to work
- Routers were created to help computers work faster and connect to each other
- Routers also help information find its way from the sender to the receiver
- Packets are small amounts of data sent over a network, which include data, source information, and destination information
- Packets are sent by the sender and received by the receiver
- Computer systems are groups of computers working together to achieve a common goal
- Computer networks are a group of interconnected devices that send and receive data
- Packet switching is when a message/file is broken up into packets and sent in any order, then reassembled by the receiving device
- A path is the network between two computing devices, and is a sequence of directly connected computing devices
- Bandwidth (measured in bits per second (BPS)) is the maximum amount of data that can be sent in a fixed amount of time on a computer network
4.2
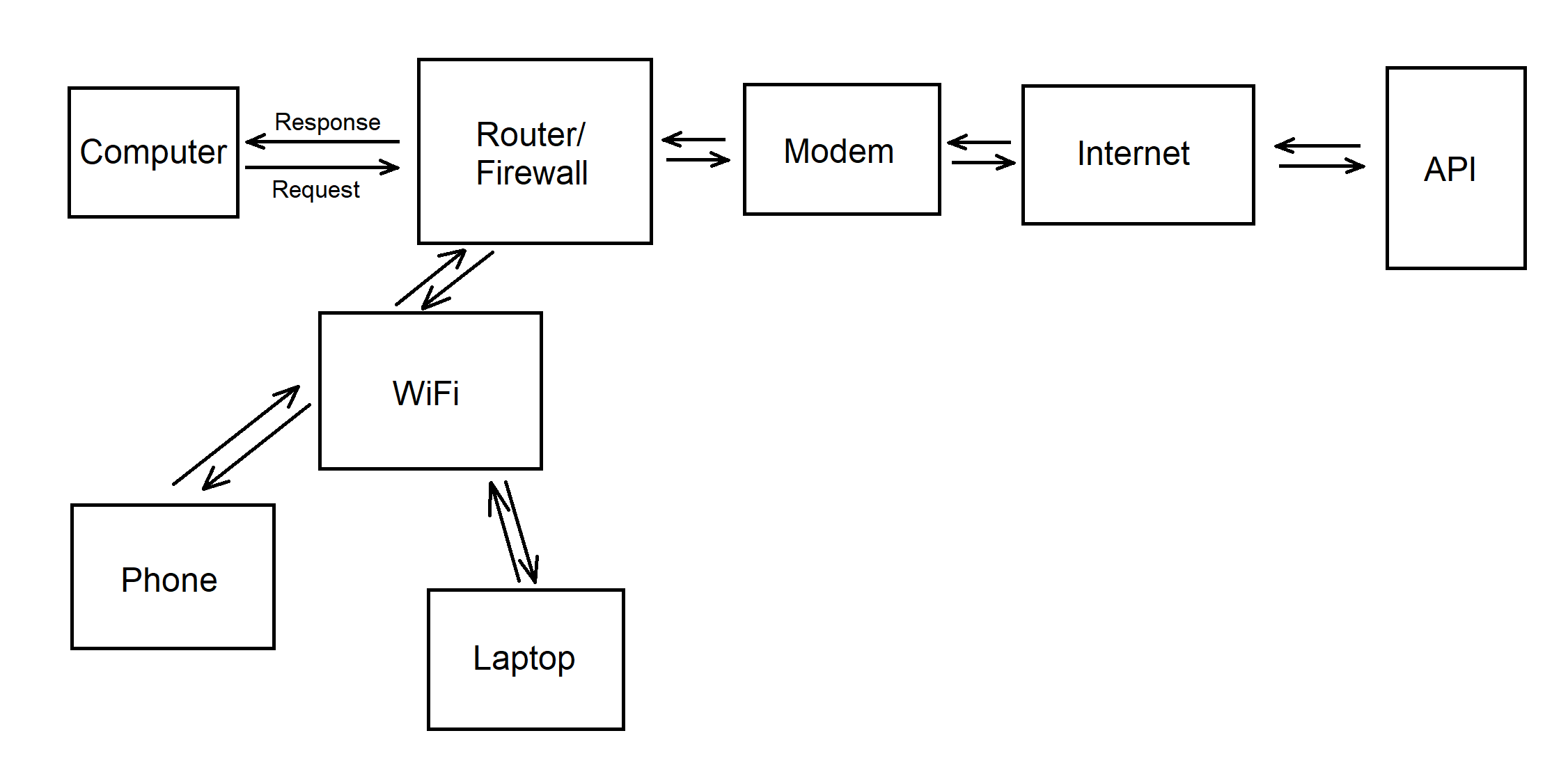
- OSI (Open Systems Interconnect) - The layers needed to go through to communicate (Application, Presentation, Session, Transport, Network, Data Link, Physical)
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) - Establishes a common standard for how to send messages between devices on the internet (Application, Transport, Internet, Network Access)
- There are many different protocols, standards, and etc. used in the Application/Transport levels, such as HTTP and DNS (OSI layers 3-7)
- Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) manages the development of internet standards via written technical discussions (Requests for Comments, RFC) in an open and collaborative process
- Network Access Layer:
- Pulls the 1’s and 0’s from a wire or radio wave, focused on hardware and protocols that carry 1’s or 0’s
- Each NIC has a unique address associated with it (Media Access Control (MAC) Address), used for local hops
- Network Access/Internet Layer Data Transmission:
- A packet contains data that is being transmitted as well as metadata containing iniformation used for routing information
- Internet Layer:
- Internet was designed to be scalable/able to change in size and scale to meet new demands
- Local Area Network (LAN) physically connects, limited by hardware and physics, 1 to hundreds of systems
- Intranet - LANs connected by routers within an organization, hundreds to thousands of systems
- Autonomous Systems (AS) - Large intranets linked together under the control and policies of major organizations, tens of thousands of systems
- The internet, millions of systems made of Autonomous Systems linked together
- Transport Layer:
- TCP does error checking and error recovery, so it is slower
- UDP performs error checking, but discards erroneous packets
- Open standards and protocols enable different manufacturers and developers to build hardware/software that can communicate with the hardware/software on the rest of the internet
- Internet/Transport Layers:
- Reliability -
- Reliability - Sender gets a receipt back, can be resended as needed
- Transport Control Protocol (TCP)
- Unreliability - Send and forget, User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
- Purpose “Port” - Number assigned to an application or survice
- 3 targets can be addressed using IP:
- Unicast - A specific device, internet wifde access; TCP is used
- Multicast - A group of devices, it is specific range of IP addresses with internet wide access, UDP is used
- Broadcast - All devices, LAN-wide, data stops at the router, and a UDP is used
- Reliability -
- Application Layer:
- Web servers - programs running on machines connected to the internet; provides web pages to clients, links to other pages using Uniform Resource Locations (URLs)
- Domain Name Service (DNS) - Applications that translate a human readable url to an IP address, holds a database of mapping of names to IPs
- Ethernet is the most popular way to access a network